afections
Retinopathy of prematurity
 DEFINItion
DEFINItion
Retinopathy of prematurity is a disease caused by immature retina, the neural tissue that covers the inside of the eye.
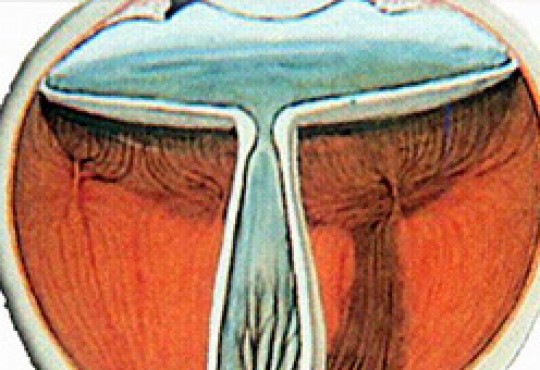
Retinopathy implies the absence of developed tissue and in some cases the presence of a fibrosis accompanied by retinal detachment.
This condition affects premature infants born with less than 1.5 kg at birth or before 32 weeks of gestation.
 symptoms
symptoms
Clinical diagnosis is based on a retinal examination performed by a pediatric ophthalmologist.
This test is always advisable for infants who weigh less than 1.5 kg at birth or who were born before 32 weeks of gestation, even if their parents do not notice anything special in the baby’s eyes.
 causes
causes
In premature or low weight babies, born before 32 weeks of gestation, there is a lack of vascularization or normal arteries and vessels. As a result, the eye has a proliferation of veins and arteries along with an extremely thin fibrous membrane. This fibrous membrane produces traction and can detach the immature retina.
This condition is also exacerbated by the high doses of oxygen required by the development of other organs in premature babies.
 treatment
treatment
The treatment is surgical, and may involve laser or cryotherapy, to the avascular retina.
Láser or cryo "burns" the abnormal retina. Then, abnormal chemical factors which induce abnormal vessel growth are inhibited.
If retinopathy is detected early enough, laser treatment or cryotherapy has a greater chance of success.
Conversely, if there is a retinal detachment, the results cannot always be satisfactory. Surgery is particularly complex if there is retinal detachment.
A child who has undergone laser treatment, can then lead a perfectly normal life if the retina is attached.
When retinopathy is not severe, it heals by itself but it is advisable to perform periodic examinations because children with retinopathy of prematurity have a higher incidence of myopia, glaucoma and strabismus.

