afections
Congenital cataract
 DEFINItion
DEFINItion
A cataract is a clouding of the lens, located inside the eye that changes shape to focus at near and far distances.
The lens is located behind the iris, the tissue that gives color to the eye.
When the lens, which under normal conditions is translucent, loses transparency and becomes opaque, it’s a cataract.
 symptoms
symptoms
The most common symptom is "blurred" vision. It may also cause photophobia or light rejection and, in exceptional cases, double vision.
 causes
causes
Normally, cataract occurs in adulthood and is due to the aging of the lens.
Rarely, the cataract may be present at birth or during the first months of life. Cataracts at this stage can constitute an emergency, occurring at the time when vision is starting to develop.
Other causes of cataract may be metabolic, such as those occurring in diabetic patients, and, rarely, trauma or infections.
 treatment
treatment
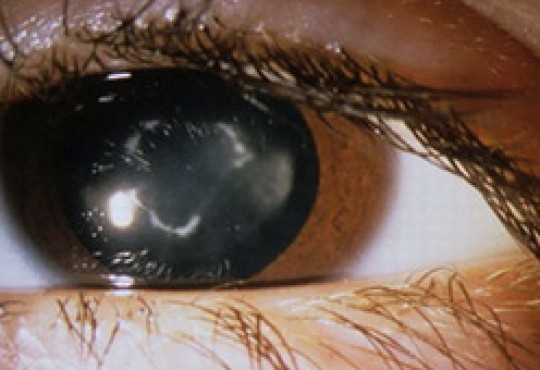
When cataract affects vision, the lens should be surgically removed.
When surgery is performed before age 2, the crystalline of the eye must be removed and replaced by a contact lens that is placed on the cornea.
After 2 years of age, an intraocular lens can be inserted, and the use of contact lens is discontinued.
To determine the power of the intraocular lens a test with ultrasound is performed. This test measures the length of the eyeball and its curvature.
FAQ
Is there a way to slow down the progression of cataract?
Unfortunately, no.
Do I have to wait until the cataract "ripens" to go to surgery? What is the best time?
It depends on the individual patient and the particular state of his/her condition.

