afections
Grave' ophthalmopathy
 DEFINItion
DEFINItion
Graves' ophthalmopathy is an inflammatory condition of the external muscles of the eye and eyelids and of the orbital fat. This produces "bulging eyes" and sometimes ocular misalignment.
 symptoms
symptoms
The most obvious symptom is "bulging eyes". There may also be foreign body sensation in the eye, caused by the difficulty to close the eyes and dry eye. Some people have double vision, caused by inflammation of the muscles and ocular misalignment. In severe cases, there may be a decrease in color vision, or fainter, grayer perception. This is a symptom of great importance since it may indicate a permanent visual impairment. Therefore, it’s an emergency.
 causes
causes
When a disease of the thyroid gland triggers a reaction in the eye, there is an inflammation of the muscles which, in turn, leads to an increase in its size. The eye and surrounding tissues are within the orbit. This is an inextensible cavity surrounded by bones, which cannot accommodate to the increase in muscle size, and the eyes are pushed out. The muscles that raise the eyelid are also affected by the condition. This generally results in the most common effect of this disorder, i.e., the retraction of the eyelids, especially, the upper eyelid. This, along with eye protrusion, causes the appearance of "bulging eyes" typical of this condition.
 treatment
treatment
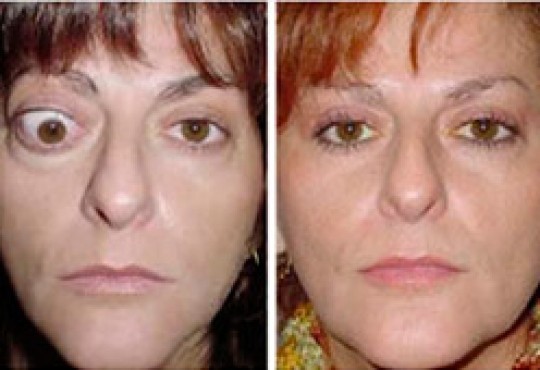
Treatment has two stages. The first stage, in which inflammation occurs in the orbital contents, lasts 6 to 12 months and resolves spontaneously.
The use of corticosteroids, at this stage, can help reduce inflammation of the muscles. The orally administered steroids have adverse general effects.
In the acute stage, steroids can be injected into the lower lid to access the orbit and reduce the inflammation typical of this disease, with minimal side-effects.
After the initial acute phase, regression of the disease starts. It’s called the chronic or cicatricial phase. Ocular and orbital sequelae can be permanent. In it, the changes in the eyes usually improve partially or completely.
Surgical treatments can correct abnormalities that persist after inflammation disappears.
Before planning a surgery, it is advisable to wait for at least six months to verify that the disease is stable.
When optic nerve compression occurs, immediate surgery is mandatory.
To correct the excessive protrusion of the eyeballs, in cases where one or both are affected, orbital decompression may be performed.
This surgery results in increased orbital volume and thus the eyes recede into position.
Treatment of double vision is accomplished by surgery on the muscles that move the eyes.
The last step in rehabilitation involves surgery on the eyelids, designed to correct their position.
It can be performed to lower the height of the upper eyelids or to correct lower eyelids.
If only orbital fat prolapse is observed, commonly known as "bags", blepharoplasty is performed to address this specific condition.
To correct the sequelae produced by thyroid eye disease or Graves ophthalmopathy, more than one surgery may be required.

